
Milliman: Fourth-Quarter Mortgage Default Risk Decreases

(Stock photo courtesy of Erik Mclean/pexels.com. Thumbnail illustration courtesy of Brett Sayles/pexels.com)
Milliman, Seattle, found a slight decrease in the lifetime serious delinquency rate (for homes 180 days or more delinquent) for U.S.-backed mortgages.
The fourth quarter 2024 Milliman Mortgage Default Index dipped to 2.12% compared to a restated 2.18% in the third quarter.
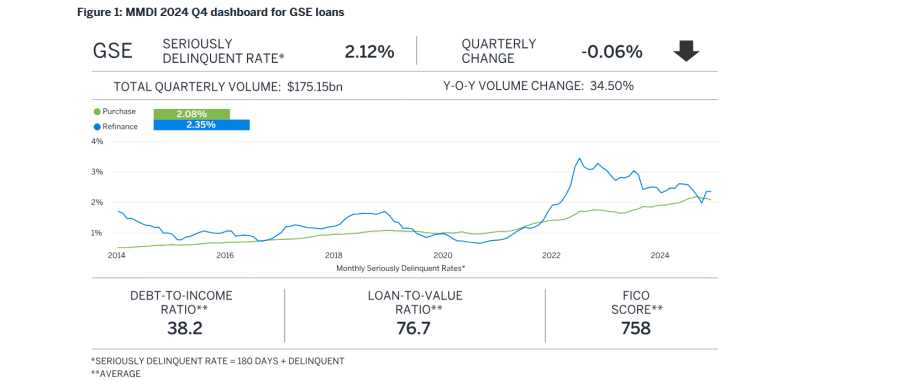
Illustration courtesy of Milliman
The decrease in default risk in the fourth quarter reflects a continued strength in borrower profiles, which include slightly higher average FICO scores and lower average loan-to-value ratios for the quarter, the MMDI said. Borrower risk decreased from 1.46% in the third quarter to 1.39% in the fourth, a shift buoyed by a lower volume of cash-out refinance loans and strong credit characteristics among purchase loans.
“Even with the slight decline in default risk this quarter, it’s important to consider how evolving economic uncertainty can impact mortgage performance,” said Jonathan Glowacki, a principal at Milliman and co-author of the MMDI. “Mortgages are long-duration contracts, and economic events can impact both new mortgages and seasoned mortgages. We will continue to monitor loan performance to evaluate how policy decisions and regulatory changes are impacting the mortgage market.”
In reviewing Q3 to Q4 changes, note that the Q3 2024 MMDI values have been restated from 2.12% to 2.18% to account for lower-than-forecasted home price appreciation. The MMDI relies on a baseline forecast of future home prices, and as projections and real-world conditions change, the values in subsequent publications adjust accordingly.
